











بندق
| إنتاج البندق عام 2016[2] | |
|---|---|
| الدولة | لإنتاج بآلاف الأطنان |
| 420.0 | |
| 120.6 | |
| 34.5 | |
| 33.9 | |
| 29.5 | |
| الإنتاج العالمي | 743.5 |
من ويكيبيديا،
| جزء من سلسلة مقالات حول |
| المطبخ العربي |
|---|
| حسب البلد˂ |
| المقادير˂ |
| الخُبز˂ |
| المشروبات˂ |
| سلطات˂ |
| أجبان˂ |
| أطباق˂ |
| مُقبلات˂ |
| أعياد ومُناسبات˂ |
| بوابة طعام |
| عنت |
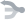
لمعانٍ أخرى، انظر بندق (توضيح).
| بندق | |
|---|---|
| حبتا بندق، بندقة بقشرة (يساراً)، بندقة بدون قشرة (يمينا) | |
| القيمة الغذائية لكل (100 غرام) | |
| حجم الحصة | 100g |
| الطاقة الغذائية | 2,629 كـجول (628 ك.سعرة) |
| الكربوهيدرات | 16.7 |
| نشا | 0.48 |
| السكر | 4.34 |
| ألياف غذائية | 11 |
| البروتين | |
| بروتين كلي | 14.95 |
| ماء | |
| ماء | 5.31 |
| الدهون | |
| دهون | 60.75 |
| دهون مشبعة | 4.464 |
| دهون أحادية غير مشبعة | 45.652 |
| دهون ثنائية غير مشبعة | 7.92 |
| الفيتامينات | |
| فيتامين أ معادل. | 1 ميكروغرام (0%) |
| فيتامين أ | 20 وحدة دولية |
| الثيامين (فيتامين ب١) | 0.643 مليغرام (49%) |
| الرايبوفلافين (فيتامين ب٢) | 0.113 مليغرام (8%) |
| نياسين (Vit. B3) | 1.8 مليغرام (12%) |
| فيتامين ب٥ أو حمض بانتوثينيك | 0.918 مليغرام (18%) |
| فيتامين بي6 | 0.563 مليغرام (43%) |
| ملح حمض الفوليك (فيتامين ب9) | 113 ميكروغرام (28%) |
| فيتامين ج | 6.3 مليغرام (11%) |
| فيتامين إي | 15.03 مليغرام (100%) |
| فيتامين ك | 14.2 ميكروغرام (14%) |
| معادن وأملاح | |
| كالسيوم | 114 مليغرام (11%) |
| الحديد | 4.7 مليغرام (38%) |
| مغنيزيوم | 163 مليغرام (44%) |
| منغنيز | 6.175 مليغرام (309%) |
| فسفور | 290 مليغرام (41%) |
| بوتاسيوم | 680 مليغرام (14%) |
| صوديوم | 0 مليغرام (0%) |
| زنك | 2.45 مليغرام (25%) |
| معلومات أخرى | |
| النسب المئوية هي نسب مقدرة بالتقريب باستخدام التوصيات الأمريكية لنظام الغذاء للفرد البالغ. | |
| تعديل مصدري – تعديل |
البندق[1] ثمرة أشجار البندق. تؤكل هذه الثمار وتعصر فيستخرج منها زيت مقبول الطعم وتعلو شجرة البندق من 3 ـ 6 أمتار، وهي ذات سوق وفروع عديدة، وأوراقها طرية بيضوية حادة الرأس مزدوجة التسنن.حب بندق
أفاد باحثون بأن المواد الغذائية الموجودة بالبندق صديقة للقلب والشرايين كونها مصدر لـ “أوميجا3” التي تمنع تخثر الدم وانسداد الشرايين، وتخفض ضغط الدم وتقلل خطورة المصابين بمرض السكري من إصابتهم بأمراض القلب.
وأشار الباحثون إلى أن البندق مادة غذائية غنية بفيتامين “إي” فهو مضاد للتاكسد ومانع للشيخوخة المبكرة، ويفيد عند انخفاض نسبة السكر في الدم أثناء فترات الحيض، مؤكدين أن فيتامين “إي” الذي يحتويه يمنع تطور مرض السكر، ينظم فعاليات القلب والشرايين والدماغ والأعصاب، مفيد في شفاء الجروح، كما يحمي من الإصابة بسرطان البروستاتا.
وأوضح الباحثون أن البندق يحتوي أيضاً على فيتامين “ب5” ، وفيتامين “ب6” الذي يقوي نظام المناعة ومفيد عند انخفاض نسبة السكر في الدم، ويحتوي على فيتامين “ب9” الضروري أثناء فترة الحمل، لأنه يقلل من المادة المسببة لانسداد الشرايين، ويقلل من خطورة الجلطة القلبية والشلل والخرف.


Hazelnut
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaJump to navigationJump to searchThis article is about the type of nut. For the type of tree, see Hazel (Corylus).Ripe hazelnutsCorylus colurna, TurkeyA sweeper gathers hazelnuts in an orchard.
The hazelnut is the nut of the hazel and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus Corylus, especially the nuts of the species Corylus avellana. It also is known as cobnut or filbert nut according to species.[1] A cob is roughly spherical to oval, about 15–25 mm (5⁄8–1 in) long and 10–15 mm (3⁄8–5⁄8 in) in diameter, with an outer fibrous husk surrounding a smooth shell and a filbert is more elongated, being about twice as long as its diameter. The nut falls out of the husk when ripe, about seven to eight months after pollination. The kernel of the seed is edible and used raw or roasted, or ground into a paste. The seed has a thin, dark brown skin, which is sometimes removed before cooking.
Hazelnuts are used in confectionery to make praline, and also used in combination with chocolate for chocolate truffles and products such as Cadbury chocolate bars, Nutella and Frangelico liqueur. Hazelnut oil, pressed from hazelnuts, is strongly flavoured and used as a cooking oil. Turkey is the world’s largest producer of hazelnuts.[2]
Hazelnuts are rich in protein, monounsaturated fat, vitamin E, manganese, and numerous other essential nutrients (nutrition table below)


History
In 1995, evidence of large-scale Mesolithic nut processing, some 8,000 years old, was found in a midden pit on the island of Colonsay in Scotland. The evidence consists of a large, shallow pit full of the remains of hundreds of thousands of burned hazelnut shells. Hazelnuts have been found on other Mesolithic sites, but rarely in such quantities or concentrated in one pit. The nuts were radiocarbon dated to 7720±110 BP, which calibrates to circa 6000 BC. Similar sites in Britain are known only at Farnham in Surrey and Cass ny Hawin on the Isle of Man.[4][5]
This discovery gives an insight into communal activity and planning in the period. The nuts were harvested in a single year, and pollen analysis suggests that all of the hazel trees were cut down at the same time.[5] The scale of the activity and the lack of large game on the island, suggest the possibility that Colonsay may have contained a community with a largely vegetarian diet for the time they spent on the island. Originally, the pit was on a beach close to the shore and was associated with two smaller, stone-lined pits whose function remains obscure, a hearth, and a second cluster of pits.[4]
The traditional method to increase nut production is called ‘brutting’, which involves prompting more of the tree energy to go into flower bud production, by snapping, but not breaking off, the tips of the new year shoots’ six or seven leaf groups from where they join with the trunk or branch, at the end of the growing season.[citation needed] The traditional term for an area of cultivated hazelnuts is a plat.
Culinary uses
Hazelnuts are used in confections to make pralines, chocolate truffles, and hazelnut paste products. In Austria, hazelnut paste is an ingredient for making tortes, such as Viennese hazelnut torte. In Kiev cake, hazelnut flour is used to flavor its meringue body, and crushed hazelnuts are sprinkled over its sides. Dacquoise, a French dessert cake, often contains a layer of hazelnut meringue. Hazelnuts are used in Turkish cuisine and Georgian cuisine; the snack churchkhela and sauce satsivi are used, often with walnuts. Hazelnuts are also a common constituent of muesli. The nuts may be eaten fresh or dried, having different flavors.[6]
Controversy
Ferrero SpA, the maker of Nutella and Ferrero Rocher, uses 25% of the global supply of hazelnuts.[7] Nearly seventy percent of the world’s hazelnuts come from Turkey where, on approximately 400,000 family-owned orchards, illegal child labour is common. This commercial product, Nutella, came under pressure after a 2019 BBC investigation found that migrant child labour is used on many hazelnut orchards in Turkey, the spread’s main supply source. Its parent company, Ferrero, has stated that, while it does run programmes aimed at removing child workers from farms, the complexity of the supply chain means it is unable to say with certainty whether or not any children pick some of its hazelnuts.[8][9]
Nutrients
In a 100-gram (3 1⁄2-ounce) reference amount, raw hazelnuts supply 2,630 kilojoules (628 kilocalories) of food energy and are a rich source (20% or more of the Daily Value, DV) of numerous essential nutrients (see table).
Hazelnuts contain particularly high amounts of protein, dietary fiber, vitamin E, iron, thiamin, phosphorus, manganese, and magnesium, all exceeding 30% DV (table). Several B vitamins have appreciable content. In lesser, but still significant amounts (moderate content, 10-19% DV), are vitamin K, calcium, zinc, and potassium (table).
Hazelnuts are a significant source of total fat, accounting for 93% DV in a 100-gram amount. The fat components are monounsaturated fat as oleic acid (75% of total), polyunsaturated fat mainly as linoleic acid (13% of total), and saturated fat, mainly as palmitic acid and stearic acid (together, 7% of total).[3]
Cultivars
The many cultivars of the hazel include ‘Atababa’, ‘Barcelona’, ‘Butler’, ‘Casina’, ‘Clark’, ‘Cosford’, ‘Daviana’, ‘Delle Langhe’, ‘England’, ‘Ennis’, ‘Halls Giant’, ‘Jemtegaard’, ‘Kent Cob’, ‘Lewis’, ‘Tokolyi’, ‘Tonda Gentile’, ‘Tonda di Giffoni’, ‘Tonda Romana’, ‘Wanliss Pride’, and ‘Willamette’.[10] Some of these are grown for specific qualities of the nut, including large nut size, or early or late fruiting, whereas others are grown as pollinators. The majority of commercial hazelnuts are propagated from root sprouts.[10] Some cultivars are of hybrid origin between common hazel and filbert.[11]
Harvesting
Hazelnuts are harvested annually in mid-autumn. As autumn comes to a close, the trees drop their nuts and leaves. Most commercial growers wait for the nuts to drop on their own, rather than using equipment to shake them from the tree. The harvesting of hazelnuts is performed either by hand or by manual or mechanical raking of fallen nuts.
Four primary pieces of equipment are used in commercial harvesting: the sweeper, the harvester, the nut cart, and the forklift. The sweeper moves the nuts into the center of the rows, the harvester lifts and separates the nuts from any debris (i.e. twigs and leaves), the nut cart holds the nuts picked up by the harvester, and the forklift brings a tote to offload the nuts from the nut cart and then stacks the totes to be shipped to the processor (nut dryer).
The sweeper is a low-to-the-ground machine that makes two passes in each tree row. It has a 2 m (6 ft 7 in) belt attached to the front that rotates to sweep leaves, nuts, and small twigs from left to right, depositing the material in the center of the row as it drives forward. On the rear of the sweeper is a powerful blower to blow material left into the adjacent row with air speeds up to 90 m/s (300 ft/s). Careful grooming during the year and patient blowing at harvest may eliminate the need for hand raking around the trunk of the tree, where nuts may accumulate. The sweeper prepares a single center row of nuts narrow enough for the harvesting tractor to drive over without driving on the center row. It is best to sweep only a few rows ahead of the harvesters at any given time, to prevent the tractor that drives the harvester from crushing the nuts that may still be falling from the trees. Hazelnut orchards may be harvested up to three times during the harvest season, depending on the quantity of nuts in the trees and the rate of nut drop as a result of weather.[12]
The harvester is a slow-moving machine pushed by a tractor, which lifts the material off the ground and separates the nuts from the leaves, empty husks, and twigs. As the harvester drives over the rows, a rotating cylinder with hundreds of tines, rakes the material onto a belt. The belt takes the material over a blower and under a powerful vacuum that sucks any lightweight soil and leaves from the nuts, and discharges them into the orchard. The remaining nuts are conveyed into a nut cart that is pulled behind the harvester. Once a tote is filled with nuts, the forklift hauls away the full totes and brings empty ones back to the harvester to maximize the harvester’s time.
Two different timing strategies are used for collecting the fallen nuts. The first is to harvest early, when about half of the nuts have fallen. With less material on the ground, the harvester can work faster with less chance of a breakdown. The second option is to wait for all the nuts to fall before harvesting. Although the first option is considered the better of the two,[13] two or three passes do take more time to complete than one. Weather also must be a consideration. Rain inhibits harvest and should a farmer wait for all the nuts to fall after a rainy season, it becomes much more difficult to harvest. Pickup also varies with how many acres are being farmed as well as the number of sweepers, harvesters, nut carts, and forklifts available.
Production
In 2017, world production of hazelnuts (in shells) was one million tonnes.[14] The hazelnut production in Turkey accounts 67% of the world total, followed by Italy, Azerbaijan, the United States, China, and Georgia.[14] The large number of hazelnut farms in Turkey and the influx of Syrian refugees have raised concerns of child labor and exploitation that is hard to track.[15]
In the United States, Oregon accounted for 99% of the nation’s production in 2014, having a crop value of $129 million that is purchased mainly by the snack food industry.[16] Expansion of hazelnut production in Ontario, Canada, occurred in 2017.[17]
In the southern hemisphere, Chile was the largest producer of hazelnuts in 2015, with most of the production exported to Europe and the United States.[18] In 2016, Chile exported 6,500 tonnes of hazelnuts.[17]
In the United Kingdom, hazelnuts are sometimes referred to as cobnuts, for which a specific cultivated variety – Kent cobnuts – is the main variety cultivated in fields known as plats, hand-picked, and eaten green.[19] According to the BBC, a national collection of cobnut varieties exists at Roughway Farm in Kent.[20] They are called cobnuts because cob was a word used to refer to the head or “noggin”, and children had a game in which they would tie a string to a hazelnut and use it to try to hit an opponent on the head

10 فوائد للبندق.. يخفض الوزن ويمنع الإمساك ويعزز صحة القلب والمخ
الثلاثاء، 09 أبريل 2019 03:44 م

قالت صحيفة Boldsky فى تقرير لها أن البندق يعتبر من المكسرات الغنية بالبروتين، والدهون، والفيتامينات، والمعادن، التي تفيد صحتك إلى حد كبير، حيث يحتوى البندق على نكهة حلوة، ويمكن أن يؤكل فى شكل خام، أو مطحون، أو مشوى، مما يجعله إضافة لذيذة للعديد من الأطباق.
يستخدم البندق كنكهة فى القهوة والمعجنات، بالإضافة إلى تناول الحلويات والأطباق اللذيذة.
القيمة الغذائية للبندق
يحتوى 100 جرام من البندق الخام تحتوي على 567 سعرة حراري، كما أنه يحتوي على 13.33 جرام من البروتين، و40 جراما من الدهون، و40 جرام من الكربوهيدرات،و 6.7 جرام من الألياف، 3.33 جرام من السكر،و 200 ملج من الكالسيوم،و 3.60 ملج من الحديد،كما يحتوي البندق على كميات جيدة من فيتامين E ، والفوسفور، والبوتاسيوم ،والزنك، والفولات والماغنيسيوم، والدهون الصحية، والنحاس، وفيتامين ب 6.
الفوائد الصحية للبندق:
يساعد فى خفض الوزن
فالبندق يعزز عملية الحرق عند تناوله، وهذا يساعد في فقدان الوزن، فزيادة التمثيل الغذائي يعني زيادة في معدل حرق السعرات الحرارية، وتحويلها إلى طاقة، ووفقا لدراسة، فإن البندق يقلل من فرص الاصابة بالسمنة، لأنه تزيد من التمثيل الغذائي، بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فإن البندق غني بالبروتين والدهون والألياف التي تعطي الشعور بالامتلاء. هذا يمنع الوجبات الخفيفة البين الوجبات، ويجعلك تشعر بالشبع لفترة أطول.
تعزيز صحة القلب
والبندق مصدر ممتاز لمضادات الأكسدة، وأحماض أوميجا 9 الدهنية التي تسهم في زيادة الكوليسترول الجيد، وخفض الكوليسترول السيئ، فهذا يساعد على منع تراكم الدهون في الشرايين ، وبالتالي تقليل خطر الإصابة بالنوبات القلبية،والسكتة الدماغية، وأمراض القلب الأخرى، وفقا لدراسة، فإن اتباع نظام غذائي غني بالبندق يقلل من خطر الإصابة بأمراض القلب والأوعية الدموية عن طريق خفض الكولسترول “البروتين الدهني منخفض الكثافة”.
منع السرطان..
يمتلئ البندق بمضادات الأكسدة القوية التي تقلل من تأثير الجذور الحرة في الجسم التي تسبب السرطان،حيث يحتوي البندق، والمكسرات الأخرى على مضادات أكسدة تسمى “برانثوسيانيد”، والتي قد تساعد في منع بعض أنواع السرطان، يعتبر البندق أيضًا مصدرًا جيدًا لفيتامين E، وهو يحتوى على مضادات الأكسدة القوية الأخرى التي تحمي من تلف الخلايا التى ترتبط بالسرطان.
علاج مرض السكري
وفقا لدراسة بحثية، يمكن أن يساعد البندق في خفض مستويات السكر في الدم، وتحسين حساسية الجسم للأنسولين، فقد تم اعطاء المشاركين مجموعة من 15 جرام من عين الجمل، 7.5 جرام من اللوز، و 7.5 جرام من البندق، ونتيجة لذلك ، كان هناك انخفاضا كبيرا في مستويات السكر بالدم، يقال إن حمض الأوليك، وهو نوع من الأحماض الدهنية في البندق، له آثار مفيدة على حساسية الأنسولين.
 يحتوى على العديد من الفيتامينات والبروتين والمعادن
يحتوى على العديد من الفيتامينات والبروتين والمعادن5. خفض الإلتهاب..
البندق يحمل خصائص مضادة للالتهابات بسبب تركيز عال من الدهون الصحية فيه، فاتباع نظام غذائي غني بالبندق قد يقلل من فرص الالتهاب لدى الأشخاص الذين يعانون من زيادة الوزن والسمنة.
6. تعزيز صحة الدماغ..
يعتبر البندق غذاء مفيدا، حيث أنه يعزز المخ، لأنه يحتوى على نسبة عالية من فيتامين (هـ) والمنجنيز، والنحاس، والفولات، حيث إن فيتامين (هـ) والماغنيسيوم يلعبان دوراً رئيسياً فى الوظيفة الإدراكية ويقللان من خطر الأمراض المرتبطة بالعمر مثل مرض الزهايمر، وشلل الرعاش، فقد أظهرت دراسة بحثية أجريت في جامعة ولاية أوريجون بالولايات المتحدة الأمريكية، إن انخفاض تركيز هذه المغذيات الدقيقة يرتبط بزيادة خطر حدوث مشاكل صحية متعلقة بالعمر.
 تعرف على اهم فوائد البندق
تعرف على اهم فوائد البندق7. تعزيز صحة العظام
وجود الكالسيوم، والماغنيسيوم، فى البندق يساهم فى صحة العظام، ويحسن البندق من كثافة المعادن فى العظام، ويقلل من فرص هشاشة العظام والتهاب المفاصل.
8. تحسين عدد الحيوانات المنوية
وفقا للجمعية الأوروبية للتكاثر البشري والأجنة، فإن تناول المكسرات مثل البندق والجوز واللوز، وما إلى ذلك، يمكن أن يحسن من جودة ووظيفة الحيوانات المنوية.
9. منع الإمساك
يحتوي البندق على نسبة عالية من الألياف، كما أن تناوله بكميات كبيرة يعزز حركة الأمعاء بانتظام ويساعد على منع الإمساك.
10. يعزز صحة الجلد والشعر
تسهم الكمية العالية من فيتامين (هـ) في البندق في تعزيز صحة البشرة والشعر، يمنع فيتامين (هـ) شيخوخة الجلد المبكرة، ويحافظ على صحة الجلد، من خلال علاج الندبات، وحب الشباب والتجاعيد.
يساعد أيضًا في نمو الشعر، ويمنع تساقطه.
 10 فوائد للبندق.. تعرف عليها
10 فوائد للبندق.. تعرف عليهاكيفية اختيار أفضل للبندق :
اختار دائمًا البندق الطازج الذي يبدو ممتلئ، وثقيل، اختار البندق الذي يكون قشرته سليمة ولامعة مع تدرج اللون البني الداكن المحمر، تجنب البندق المحتوى على شقوق أو ثقوب.






